THE PLUS RHINOPLASTY IN KOREA
Rhinitis and Sinusitis Rhinoplasty in Korea


THE PLUS RHINOPLASTY IN KOREA
Rhinitis and Sinusitis Rhinoplasty in Korea
the plus rhinoplasty IN kOREA
Rhinitis and Sinusitis Surgery
Patients with nasal conditions such as rhinitis and sinusitis often face unique considerations when planning for nasal surgery. By carefully evaluating the patient’s medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination, our experienced team at THE PLUS Plastic Surgery determines the most appropriate course of action.
What is Rhinitis?
Rhinitis is a condition characterized by inflammation in the nasal mucosa, leading to symptoms such as excessive sneezing, nasal congestion, and a runny nose. It can be broadly categorized into allergic rhinitis and non-allergic rhinitis. Most patients with rhinitis often have complex causes.
Allergic Rhinitis is triggered by an allergic reaction of the immune system and, if left untreated, can develop into chronic or hypertrophic rhinitis. Non-Allergic Rhinitis, on the other hand, occurs due to infections, abnormalities in the hormone secretion system, deviated nasal septum, hypertrophy of the inferior turbinate, and other non-allergic reasons.
Diagnosing Rhinitis
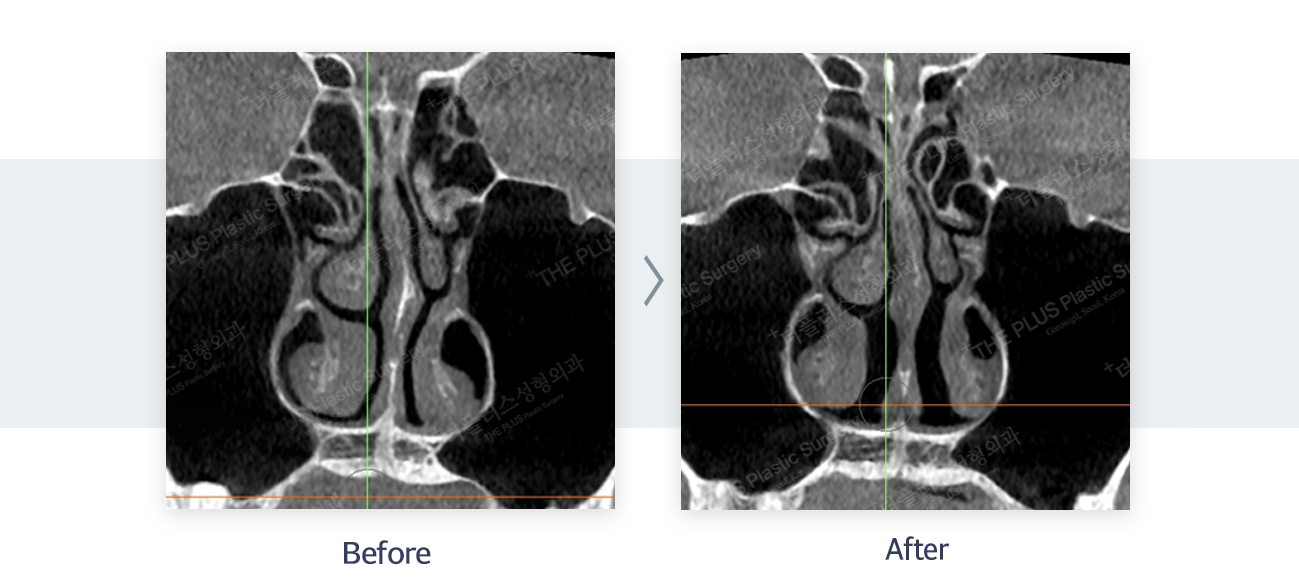
During the pre-surgery consultation, we can identify structural problems related to symptoms through a detailed history and simple inspection of the patient’s symptoms. We also confirm the patient’s response to symptoms using a swab or Cottle test (checking if it is easier to breathe when pulling the side of the nose outward). For more accurate tests, we use radiological examinations such as CT.
We conduct a Nasal Speculum Examination, a physical examination of the inside of the nose, using a nasal speculum during the consultation. We also perform an Endoscopic Examination by spraying a local anesthetic and mild mucosal vasoconstrictor in the nasal cavity for observation.
Considerations for Nasal Surgery in Patients with Nasal Diseases
For patients with nasal diseases such as rhinitis and sinusitis, the decision to proceed with nasal surgery is based on the patient’s medical history and physical examination. We may administer medication for inflammation relief before surgery. Allergic rhinitis is not a contraindication for cosmetic nasal surgery, so we can plan surgery while concurrently treating the symptoms. Rhinitis caused by structural problems in the nose is treated by nasal surgery, so surgery is rather recommended. Antibiotics are mainly effective for bacterial sinusitis, and if symptoms such as runny nose, sneezing, coughing, headache, facial pain, and fever persist for more than 2 weeks after onset, it is advisable to carefully consider nasal surgery as it can be seen as a worsening of acute or chronic sinusitis.
Understanding Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as sinusitis, is a common disease. The sinus is a cavity inside the maxillary bone located next to the nose. Normal adults catch a cold several times a year, and in more than 80% of cases, the sinuses are invaded, and about 1% of them progress to acute bacterial sinusitis. The condition in which purulent fluid accumulates inside the sinus is commonly referred to as ‘sinusitis’.
Diagnosing Sinusitis
The diagnosis of sinusitis is made by combining the patient’s symptoms and medical history, physical examination, nasal examination including endoscopy, CT and other radiological examinations. Especially, tenderness and purulent nasal discharge in physical examination are important clues for the diagnosis of acute sinusitis.
Classification and Treatment of Sinusitis by Duration
Acute sinusitis lasts less than 4 weeks, and the inflammatory process is reversible, so it can be completely recovered without sequelae through drug treatment. Subacute sinusitis lasts from 4 weeks to 12 weeks, and the inflammatory process is reversible, so normal recovery is possible through drug treatment. Chronic sinusitis refers to cases where symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks and surgical treatment is needed when there is no improvement with medication.
View the research papers from The Plus Plastic Surgery medical team.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of nasal conditions can be treated with surgery at THE PLUS Plastic Surgery in Gangnam?
At THE PLUS Plastic Surgery in Gangnam, we specialize in treating conditions such as rhinitis and sinusitis. Rhinitis, whether allergic or non-allergic, and structural issues like deviated nasal septum or hypertrophy of the inferior turbinate, can be addressed effectively through our surgical options. We tailor treatments based on thorough evaluations of your medical history and specific nasal issues.
Why should I consider having nasal surgery in South Korea, specifically at THE PLUS PS in Gangnam?
South Korea is renowned for advanced medical practices and skilled surgeons, especially in the field of cosmetic and functional surgeries. THE PLUS Plastic Surgery in Gangnam offers cutting-edge technology, experienced medical professionals, and individualized care. We ensure comprehensive pre-surgical evaluations and follow-up to achieve optimal outcomes for patients experiencing rhinitis and sinusitis.
How does THE PLUS PS determine the right surgical approach for rhinitis and sinusitis?
At THE PLUS PS, we start with a detailed assessment of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. We perform tests such as the Cottle test, nasal speculum examination, and endoscopic examination with local anesthetics to identify structural problems. Additional radiological assessments, like CT scans, help us to provide a personalized treatment plan that addresses both functional and cosmetic needs.
